What are Accelerometers?
An accelerometer is an inertial sensor that measures the acceleration of an object. It provides understanding of phenomena such as vibration and shock by appropriate processing of acceleration data. Epson's accelerometer can detect direct current (DC, 0Hz) acceleration, which allows them to measure constant acceleration and gravitational acceleration. This capability makes it possible to determine the orientation or posture of an object.
Types of Accelerometers
Accelerometers are classified into five types according to detection method.
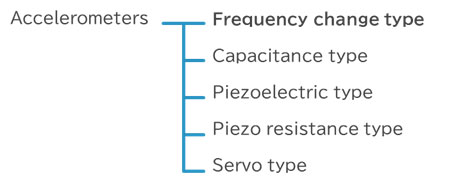
- Frequency change type
It detects acceleration by the resonant frequency change of the sensor element and is used for structural monitoring and seismographs because of high stability and high resolution by using a tuning fork structure with a high Q-value. Epson's acceleration sensor is this type and uses a crystal-based bi-tuning fork element to obtain highly accurate measurement data. - Capacitance type
It is used for automobile body control because it is suitable for low acceleration measurement and easy to realize self-diagnostic function. - Piezoelectric type
It is used for automobile collision detection, equipment vibration measurement and drop tests because it is suitable for high-frequency measurement and high-acceleration measurement. - Piezo resistance type
Low cost is realized by mass production based on MEMS technology, which is widely used in games and mobile devices. - Servo type
Good low-frequency phase characteristics, used for seismic observation and structural monitoring.
Documents about the basics and usage of accelerometers
You can download documents of the basics, selection, and usage of accelerometers.
13 items to consider when selecting accelerometer and 4 items of particular importance
Measurement data and analysis of low-speed rotation device with an accelerometer
Measurement data and analysis of bearing deterioration with an accelerometer
Measurement data and analysis of the World's Largest Caldera, Mt. Aso with an accelerometer
How Accelerometers Work
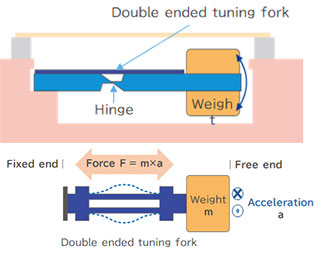
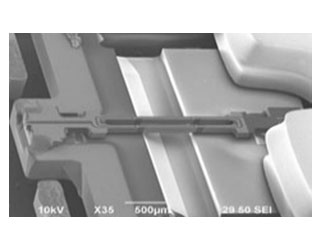
Inside the acceleration sensor there is a hammer and a sensor element. Epson uses a double-ended tuning fork quartz crystal oscillator: see below. When the weight moves, a compressive or tensile force is generated in the sensor element. We utilize the change in resonant frequency caused by these compression and stretching forces.
Documents about the basics and usage of accelerometers
You can download documents of the basics, selection, and usage of accelerometers.


13 items to consider when selecting accelerometer and 4 items of particular importance
Measurement data and analysis of low-speed rotation device with an accelerometer
Measurement data and analysis of bearing deterioration with an accelerometer
Measurement data and analysis of the World's Largest Caldera, Mt. Aso with an accelerometer
Differences Between Accelerometers and Gyro Sensors
An accelerometer is a sensor that measures the linear acceleration occurring with an object. Phenomena that can be detected include vibration, tilt, and linear motion. Linear acceleration is expressed in (m/s2).
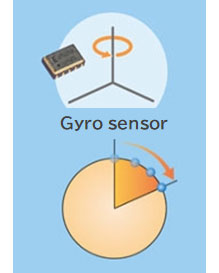
A gyro sensor is a sensor that measures the speed at which an object rotates. The speed of rotation is expressed as angular velocity (°/s) or (°/h).
Documents about the basics and usage of accelerometers
You can download documents of the basics, selection, and usage of accelerometers.


13 items to consider when selecting accelerometer and 4 items of particular importance
Measurement data and analysis of low-speed rotation device with an accelerometer
Measurement data and analysis of bearing deterioration with an accelerometer
Measurement data and analysis of the World's Largest Caldera, Mt. Aso with an accelerometer




