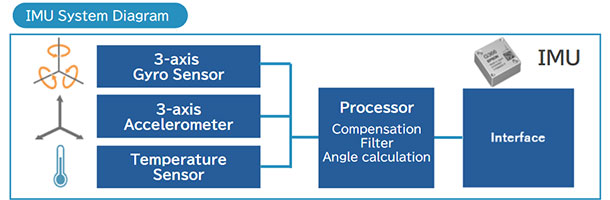
What are Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs)?
Inertial Measurement Units (IMUs) are devices that measure the angular velocity and linear acceleration in three axes of motion. They are equipped with three-axis angular velocity (gyroscope) sensors, three-axis linear acceleration sensors, and a temperature sensor for measuring three-dimensional inertial motion (translational motion and rotational motion along three orthogonal axes). They measure linear acceleration and angular velocity with high accuracy to understand and enable control of attitude and trajectory for a moving body.
Documents about "What are IMUs?"
This documents summarizes the basics of IMUs to assist you in their selection.
- What are IMUs?
- Types of IMUs
- Difference from sensor devices
- Main applications
- Features and product lineup of Epson IMUs


Types of IMUs
Example of gyro sensors used in IMUs
- Ring Laser Gyroscope method
- Fiber Optical Gyroscope method
- MEMS (Micro Electro Mechanical System ) method
Epson's IMUs incorporate Quartz-MEMS gyro sensors that combine unique double-T structure elements made of quartz crystal with precision processing technology to achieve highly accurate and stable output.
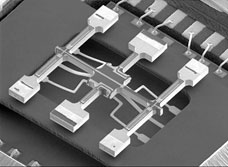
Differences from Sensor Devices
IMUs : High-precision data can be output stably by various internal compensation and calculations.
Sensor Devices : The performance of the individual device is good, but the functions are not linked between each sensor.