Gyro sensors - What is Gyro Sensors?
Gyro sensors
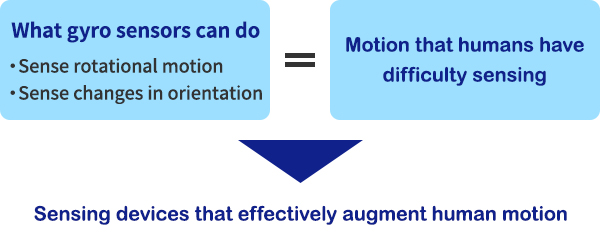
Gyro sensors, also known as angular rate sensors or angular velocity sensors, are devices that sense angular velocity.
Angular velocity
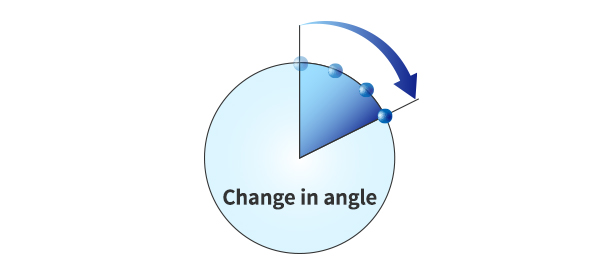
In simple terms, angular velocity is the change in rotational angle per unit of time.
Angular velocity is generally expressed in deg/s (degrees per second).
Gyro Sensor Types
Gyro sensors come in a variety of types. Here, different types are plotted by size and performance.
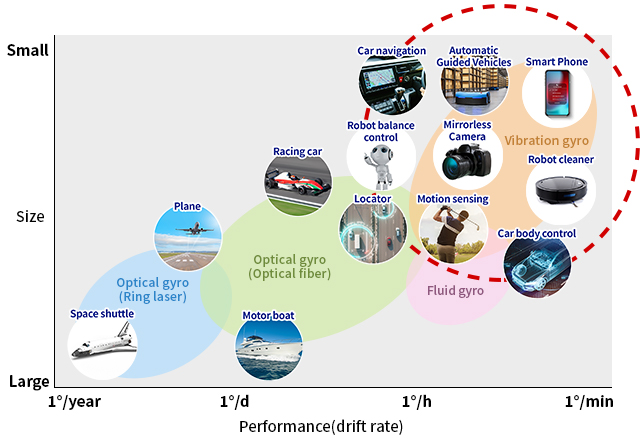
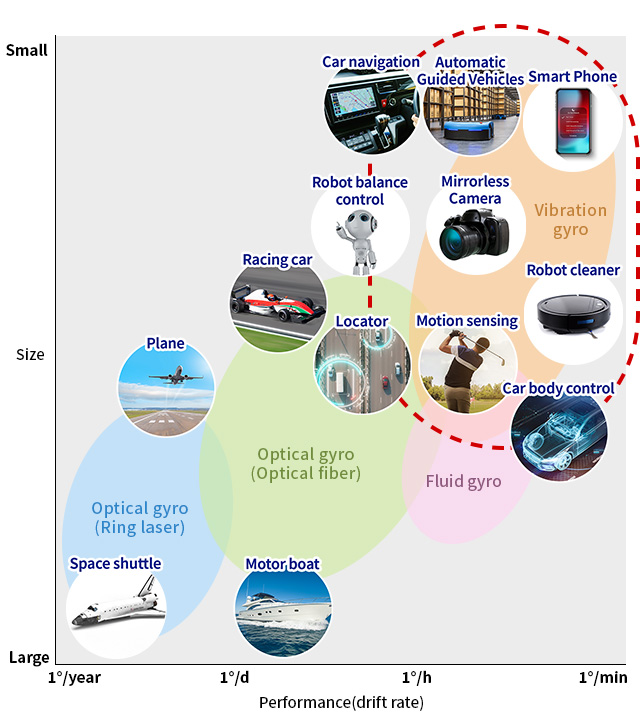
Miniature, high-accuracy vibration gyro sensors are indipensable.
In recent years vibration gyro sensors have found their way into mirrorless / SLR cameras, vehicle electronic stability control (anti-skid) systems and among other things.
Vibration Gyro Sensors
Vibration gyro sensors sense angular velocity from the Coriolis force applied to a vibrating element. For this reason, the accuracy with which angular velocity is measured differs significantly depending on element material and structural differences. Here, we briefly describe the main types of elements used in vibration gyro sensors.
Types of elements used in vibration gyro sensors
Vibration gyro sensor manufacturers are using a variety of materials and structures in an effort to devise compact, high-accuracy gyro sensors that have good characteristics, including:
- scale factor
- temperature-frequency coefficient
- compact size
- shock resistance
- stability
- noise characteristics
| Material | Sample Structure | |
|---|---|---|
| Piezoelectric transducer |
Crystal 
|
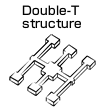 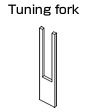 
|
| Silicon transducer |
Silicon 
|
Si MEMS NOTE: Every company uses a different structure. |
| Piezoelectric transducer | |
|---|---|
| Material | Sample Structure |
|
Crystal 
|
  
|
| Silicon transducer | |
|---|---|
| Material | Sample Structure |
|
Silicon 
|
Si MEMS NOTE: Every company uses a different structure. |
How Angular Velocity Sensing Works in Vibration Gyro Sensors
Vibration gyro sensors sense angular velocity from the Coriolis force applied to a vibrating object.
Here, we explain how this works, using as an example Epson 's double-T structure crystal element.
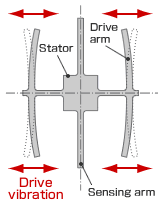
1. Normally, a drive arm vibrates in a certain direction.
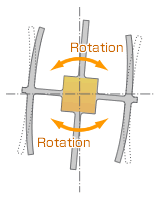
2. Direction of rotation
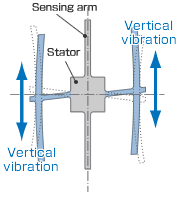
3. When the gyro is rotated, the Coriolis force acts on the drive arms, producing vertical vibration.
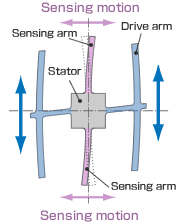
4. The stationary part bends due to vertical drive arm vibration, producing a sensing motion in the sensing arms.

5. The motion of a pair of sensing arms produces a potential difference from which angular velocity is sensed. The angular velocity is converted to, and output as, an electrical signal.
Gyro Sensor Applications
There are three main applications for gyro sensors.
Angular velocity sensing
Sense the amount of angular velocity produced.
Used in measuring the amount of motion itself.
Ex.) Checking athletic movement
Angle sensing
Senses angular velocity produced by the sensor's own movement. Angles are detected via integration operations by a CPU.
The angle moved is fed to and reflected in an application.
Ex.) Car navigation systems
Game controllers
Cellular
Control mechanisms
Senses vibration produced by external factors, and transmits vibration data as electrical signals to a CPU.
Used in correcting the orientation or balance of an object.
Ex.) Camera-shake correction
Vehicle control
Sample applications
-
SmartPhone
Motion sensing
-
Robot balance control
Attitude control
-
Driving locator

Stability control
-
Car navigation

Dead reckoning
-
Sports sensors

Motion sensing
-
Automatic Guided

Straight control
-
Drone

Attitude control
-
Mirrorless camera

Stabilization